USAID INGOBYI ACTIVITY
The United States Agency for International Development (USAID) Ingobyi Activity[1] is a five-year cooperative agreement to improve the quality of reproductive, maternal, newborn, and child health (RMNCH) and malaria services sustainably, to reduce infant and maternal mortality in Rwanda. The Activity builds upon the tremendous gains Rwanda has made in the health sector, as well as previous USAID investments.
Ingobyi Activity’s efforts aim to reduce infant and maternal mortality and the incidence of malaria in Rwanda by improving the availability, quality, and utilization of RMNCH and malaria services with resilience and toward sustainability. The Activity partners with the Government of Rwanda (GOR) to build on the country’s considerable achievements, guided by national health strategies, goals, objectives, and data. Beyond building capacity and capability, the Activity focuses on achieving a shared understanding of the patterns and systemic structures that underlie the health system and where and how to bring about measurable, sustainable improvements. Ingobyi Activity focuses on three intermediate results (IRs), as outlined in Table 1.
Table 1: USAID Ingobyi Activity results framework
To deliver these IRs, Ingobyi Activity applies a strategic, results-oriented, and multipronged technical approach that addresses key bottlenecks and inspires the health system to respond to the RMNCH and malaria prevention and treatment needs of the Rwandan population. The Activity works with the GOR to improve the availability, quality, and utilization of RMNCH and malaria services. Technical support, provided at all levels of the health system, is based on national policies, clinical protocols, and global evidence relevant to integrated reproductive health/family planning (FP), maternal health, neonatal health, child health, and malaria prevention and treatment. The strategy is built upon the understanding that Rwandan experience and leadership, supported by the Activity’s resources and knowledge, will strengthen the health system and the services it provides to contribute to a healthier population more effectively. Interventions delivered by Ingobyi Activity to achieve the expected results include the following, among others:
- Competency-based skill-building through clinical training and mentorship. This is a tailored approach aimed at developing a cadre of district-based mentors. Using an on-site “Low Dose High Frequency” (LDHF) training approach, Ingobyi staff and professional associations provide training and mentorship to health providers at district hospitals, who in turn conduct mentorship for health center (HC) providers.
- Health systems strengthening. This effort supports district health units (DHUs) in organizing regular district health management team (DHMT) meetings to discuss, prioritize, and respond to key health challenges. It also involves strengthening the referral system to improve case management; advocating for improved infrastructure, human resources, and equipment maintenance; contributing to the development of policies and guidelines; and integrating continuous quality improvement (QI) across all services.
- Training community health workers (CHWs) on community-level packages, including integrated community case management (ICCM), community-based maternal and newborn health (CBMNH), and the community-based program on family planning (CBP-FP).
- Infection prevention and control (IPC), including the prevention of nosocomial infections; preparedness; and the prevention of infectious diseases, such as Ebola virus disease and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), at facility and community levels to reduce preventable causes of morbidity and mortality. Efforts include experienced medical specialists delivering training and clinical mentorship to health providers.
- Promoting healthy behaviors and creating demand through radio broadcasts (drama series, talk shows, and mentions), community outreach regarding integrated RMNCH and malaria messaging and service delivery, and health communication for clients at the health facility level.
Ingobyi Activity promotes globally approved high-impact RMNCH and malaria interventions to increase access to high-quality services for mothers, newborns, children, and adolescents. In maternal health, Ingobyi promotes antenatal care (ANC); postnatal care (PNC); emergency obstetric and newborn care (EmONC); safe Caesarean sections; respectful maternity care; the management of preeclampsia/eclampsia; the prevention and management of postpartum hemorrhage (PPH); postpartum family planning (PPFP); and obstetric fistula screening and repair. For newborn health, the Activity promotes essential newborn care (ENC), helping babies breathe (HBB), essential care for every baby, essential care for small and sick babies, and family-centered care. For child health, emergency triage, assessment, and treatment plus admission care (ETAT+); integrated management of childhood illness (IMCI); and ICCM are promoted, while in malaria, the Activity promotes improved diagnostic services, the management of malaria in pregnancy and of severe malaria, and home-based care interventions. Additionally, Ingobyi promotes comprehensive education and counseling that emphasizes voluntarism and choice in FP. Ingobyi Activity works with health providers to ensure that essential youth-friendly services are available and provided to young people (including at facility youth corners). These services include counseling; providing contraceptives, including emergency contraceptives; and managing sexual and gender-based violence (GBV), including providing post-exposure prophylaxis for HIV. The Activity also equips health centers with needed health communication materials and tools.
Geographic Coverage
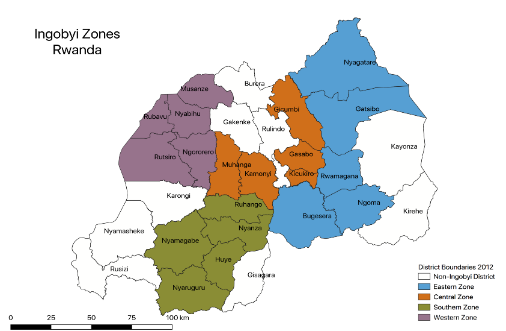
Figure 1: Map showing Ingobyi-supported districts by zone
USAID Ingobyi Activity is implemented in 20 districts that were selected by the Ministry of Health (MOH) based on key health indicators. The districts are grouped into zones to facilitate coordination and implementation (Figure 1). The RMNCH and malaria interventions are implemented in all 20 districts, while some other interventions are implemented at the national or central level only. Central-level interventions include participation in technical working groups (TWGs); policy development; and activities that respond to national maternal, newborn, and child health (MNCH); FP; and malaria priorities. District-level interventions include but are not limited to, technical assistance and support to DHMTs, communities, facilities (hospitals, health centers, and health posts), and health providers.
For the Ingobyi Activity, Urunana DC mainly contributes to Sub IR 1.2 Improved health-seeking behaviors for RMNCH/Malaria services where main activities include: incorporating SBC messages into Urunana radio soap opera, the radio magazine program, radio sketches and community outreach skits, and testing and evaluating messaging for healthy behaviors through Audience surveys.
[1] USAID Ingobyi Activity is also referred to in this report as the Activity, Ingobyi Activity, or simply as Ingobyi.
